Business Email Compromise (BEC) has plagued companies for years, yet many small businesses continue to assume they are powerless against these attacks. This misconception could not be further from the truth. Today, robust tools and simple best practices exist that can significantly secure your inbox—and your bank account—at minimal cost and effort.
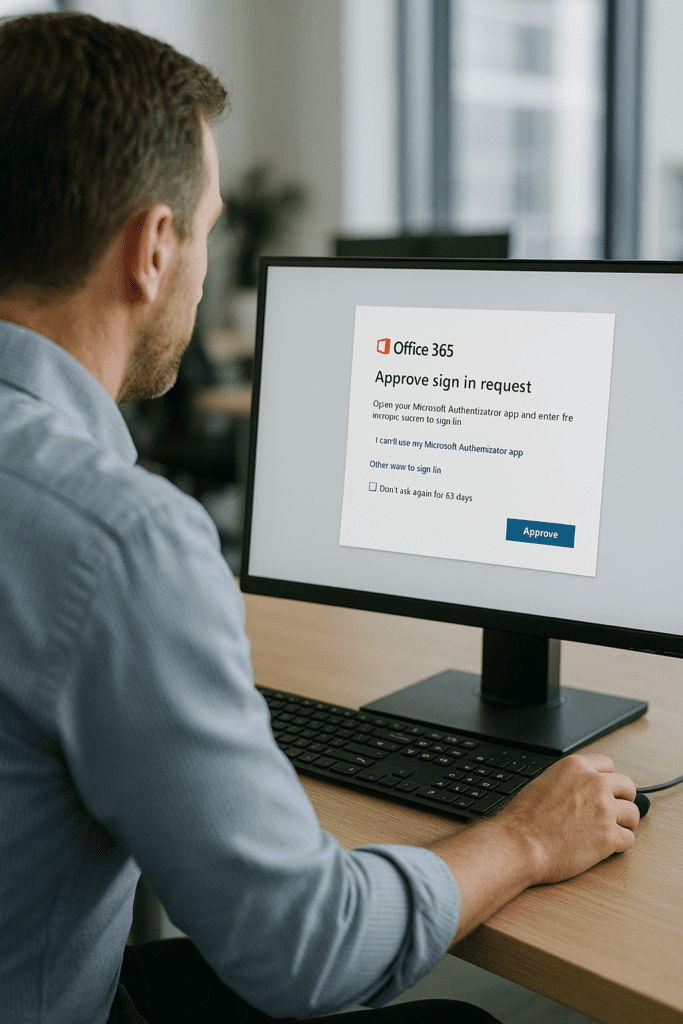
Recently, WatchPoint IT was called in to handle a particularly inventive email compromise case, highlighting the increasingly creative tactics scammers employ to monetize compromised accounts. Traditionally, attackers hijack emails to trick internal teams or clients into altering ACH or wire transfer information, redirecting payments into fraudulent accounts. Fortunately, most finance teams have become wary, routinely double-checking transactions.
However, attackers are constantly adapting.
In this recent incident, the attack began innocuously. The user received an expected email from their landlord about an updated lease agreement. The timing was perfect—the company was actively renegotiating their lease. Unfortunately, the landlord’s email account had already been compromised by the attacker, who patiently monitored conversations before inserting themselves seamlessly into the dialogue.

The unsuspecting user clicked a malicious link, believing they were securely logging into their Office 365 account to view the updated lease. Behind the scenes, the attacker employed Evilginx, a sophisticated man-in-the-middle attack that bypasses Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) by intercepting credentials directly through the user's browser. Instantly, the email account was compromised without raising immediate alarms.
Typically, compromised emails lead directly to financial theft. However, this scenario had an unusual twist—one we had never personally encountered before. With the user's credentials, scammers breached the user's LinkedIn and Indeed accounts (the same username-password combination, unsurprisingly) and started posting fraudulent job openings on the company’s behalf.
Before long, "new employees" were hired remotely, believing they had genuinely secured employment. Neither the landlord nor the compromised company had any idea that their systems and identities had been exploited. The attackers cleverly concealed their activities, creating automated rules to quietly redirect and hide their communications.
These newly hired "employees" were informed they needed special equipment to start working remotely. To make things seem legitimate, the scammers mailed each new hire a convincing check for $13,500, instructing them to deposit the funds and use their personal credit cards to purchase the equipment through a provided link.
The unsuspecting new hires eagerly deposited the checks, promptly bought the equipment, and waited. But of course, the purchased equipment never arrived, and the checks ultimately bounced, leaving these victims financially devastated and confused.

Remarkably, the compromised company initially remained oblivious. It wasn’t until these confused and frustrated "new hires" began repeatedly contacting the company’s front office that suspicions arose. Initially dismissed as spam, the receptionist eventually escalated the unusual calls to management. Only then did the tangled web of deception begin to unravel.
WatchPoint was brought in for remediation, uncovering the full extent of the breach and helping the company clean up and secure their digital environment.
The sobering reality of this incident underscores how critical pro-active email security measures are. MFA alone, while important, is no longer sufficient due to sophisticated threats like Evilginx. Businesses must consider additional layers of protection, including automated monitoring systems that detect and lock compromised accounts, third-party identity providers, or a strategic combination of both.
Ignoring these precautions because you believe it "won't happen to you" could be costly. Don’t wait for an incident like this to hit your company; act now to secure your business, protect your employees, and maintain your reputation.
Remember, cybersecurity isn’t just about technology—it's about vigilance, preparedness, and taking threats seriously before they become your reality.
CAPTCHA prompts have become a familiar sight online. CAPTCHA prompts are designed to differentiate human users from automated bots, keeping websites secure. Unfortunately, cybercriminals are now using fake CAPTCHAs as a new vector for attacks. Recently, organizations have experienced incidents involving malicious CAPTCHAs that trick users into unintentionally running harmful commands on their computers. Here is what you need to know to stay safe.
A recent WatchPoint security incident involved a sophisticated form of attack using deceptive CAPTCHA prompts. In this type of attack, a fake CAPTCHA asks users to complete unusual steps—like opening a Windows command prompt or running a PowerShell command—actions a legitimate CAPTCHA would never require. When users follow these malicious instructions, they unknowingly execute scripts that install malware, steal sensitive information, or gain remote access to their computers.
SentinelOne, WatchPoint's MDR platform, caught and isolated the attack immediately. Less sophisticated AV may not detect this as malicious behavior as there are no files immediately dropped classifying this type of attack as fileless.

Specifically, these fake CAPTCHAs typically instruct users to:
These pasted commands usually trigger malware downloads, provide attackers with remote access, or compromise sensitive data.
Fake CAPTCHA attacks first appeared in the late twenty teens, but in late 2024 and into 2025 they have surged in popularity among hackers. Security media outlets started reporting more of these attacks being seen in the wild in early 2025.

These attacks are dangerous precisely because they exploit trust. Users have grown accustomed to solving CAPTCHAs to verify their identity on various websites, making them less suspicious of CAPTCHA requests. Attackers leverage this familiarity to deceive even vigilant users.
Once executed, these malicious scripts can lead to severe consequences, including:
Legitimate CAPTCHAs will never:
Any CAPTCHA prompt asking you to perform these actions should immediately raise suspicion.
To prevent falling victim to malicious CAPTCHA attacks, follow these simple guidelines:
To help spread awareness within your organization, feel free to use the following email as a communication template:
Subject: Security Awareness: Beware of Malicious CAPTCHA Prompts
Team,
Recently, we had an incident involving fake CAPTCHAs prompting users to execute commands on their computer. To avoid this:
Remember: R for Run and tell IT.
Your awareness helps keep us secure. If something feels off, reach out to us right away.
Thank you,
[Your IT Security Team]
Final Thoughts
Cyber threats evolve constantly, and staying informed is your strongest defense. By recognizing and avoiding suspicious CAPTCHA prompts, you can help maintain the security of your organization’s data and IT infrastructure. Always trust your instincts—if something doesn’t feel right, pause and verify with IT support.
Stay safe, stay vigilant!
Would you ever hang a bright neon sign outside your business reading, "Hey burglars, doors unlocked, come on in!"? Of course not. Yet astonishingly, many businesses do just that digitally, leaving their firewall ports wide open and welcoming cybercriminals with open arms. Recently, even the FBI stepped in to issue a stern (and somewhat embarrassing) Open Port Warning about the dangers of leaving these digital doors unlocked. And while cybersecurity is serious business, sometimes the simplicity of the problem borders on comedy, until it’s not funny at all.
In the recent cybersecurity advisory (Alert Code: AA25-050A), the FBI and CISA (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency) issues a joint advisory sounding the alarm about cybercriminals actively targeting networks through open firewall ports. Think of it like leaving your office windows wide open overnight, one forgotten latch and intruders can waltz right in. The FBI is urging businesses to close these vulnerabilities immediately, before your open ports become a hacker's personal playground filled with data breaches, ransomware, and other digital nightmares.

Let's be honest: leaving your ports open is like tossing your car keys into the front seat and walking away. Sure, your car might be there in the morning, but the odds aren't exactly in your favor. The puzzling thing? Checking for open ports is straightforward, yet countless businesses overlook it, creating massive and entirely unnecessary risks. The potential cost isn't just financial; imagine explaining to your clients that your "secure" network was basically a revolving door for hackers. Ouch.
Like many other cyber security topics, business leaders choose to ignore them even with plenty of coverage on the subject. Here are just a few of the articles written about this particular warning.
Forbes: "FBI Says Backup Now—Advisory Warns Of Dangerous Ongoing Attacks"
This article highlights the FBI's warning about the ongoing and dangerous nature of Ghost ransomware attacks, emphasizing the importance of immediate data backups.
WaterISAC: "(TLP:CLEAR) CISA, FBI, and MS-ISAC Release Advisory on Ghost (Cring) Ransomware"
This piece provides an overview of the joint advisory, detailing the indicators of compromise (IOCs), tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) associated with Ghost ransomware.
Security Boulevard: "[CISA AA25-050A] #StopRansomware: Ghost (Cring) Ransomware"
This article discusses the CISA advisory on Ghost ransomware and introduces an attack graph released by AttackIQ to help organizations validate their security controls against this threat.
SafeBreach: "SafeBreach Coverage for US CERT AA25-050A [Ghost (Cring) Ransomware]"
This blog post outlines how SafeBreach has added coverage against attacks by Ghost threat actors targeting organizations across more than 70 countries.
NeptuneWorx: "Summary: Understanding CISA's Cybersecurity Advisory AA25-050A"
This summary provides insights into the CISA advisory, emphasizing the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures and understanding the threat landscape.
We don’t have the hard statistics yet for 2025, but over the past several weeks at WatchPoint we have been getting more requests than usual for help with ransomware attacks. These were non-WatchPoint clients of course and generally referrals from existing clients, but of the last three, two were caused by open ports. There was a dip in ransomware attacks that coincided with the start of the war in Ukraine, but now we appear to be back in the throughs of a full-on assault from cyber attackers.
Here’s the good news—checking your ports isn't complicated or time-consuming. In fact, it's as quick and painless as checking your smartphone’s battery. With a few clicks, we can run a port scan and immediately see if you are unintentionally offering hackers a warm welcome to your network. Given how simple this task is, there’s really no excuse not to do it unless you enjoy making life easy for cybercriminals.
At WatchPoint IT, our mission is to make cybersecurity feel less like rocket science and more like routine maintenance—easy, stress-free, and efficient. Our free port scanning service quickly identifies which of your digital doors are wide open. Additionally, we won’t leave you hanging. We provide continuous monitoring and alerts to immediately flag any new vulnerabilities, keeping your digital assets safe 24/7.
Here's What You'll Receive from Our Free Scan:
Cybersecurity can seem daunting, packed with acronyms, jargon, and endless threats. But when it comes to securing your network, think of it as simply locking your front door. With the FBI’s urgent warning fresh in our minds, there’s no better time than now to act.
Don’t wait until you’re already compromised. Connect with WatchPoint IT today, run your free port scan, and let’s lock those digital doors tighter than Fort Knox. Because in cybersecurity, being proactive isn't just smart, it's essential.
Stay smart, stay secure!
Ready to lock things down? Visit WatchPoint IT today and let us know you would like a free port scan. Your future self will thank you.
Losing access to your business’s data – even temporarily – is a nightmare worthy of a horror movie.

The basic function of data backup tools is to create copies of your data and store them in a safe place. If something goes wrong, recovery tools will use these copies to restore your lost files.
So, if your business already uses backup and recovery tools, you would think your data is safe… but this isn’t necessarily true.
A new report shows that some backup tools aren’t as reliable as they should be. In fact, a third of all data losses are caused by backup-related issues. When people try to recover data, they discover it’s been lost, corrupt or was never backed up in the first place.
One of the biggest threats to businesses right now is ransomware. This is a type of malicious software (or "malware") that locks you out of your files unless you pay a ransom to regain access.
The report found that half of businesses using backup tools still ended up paying ransoms to retrieve their files, because it was faster than trying to use their own recovery tools. Even worse? Only a small number of businesses that paid ransoms were able to fully recover their data.
Often, it’s because they haven’t been set up properly. And even when they are, they still need to be verified regularly to make sure they are still backing up your files.
Also, older backup and recovery tools can’t keep up with today’s sophisticated cyber-attacks. Ransomware will target the backup files as well as the production files to make it impossible to recover them. Backup files need to be properly encrypted and separated from the production data. Setting up and maintaining a reliable backup system is straightforward if you have been doing it for 25 years. IT experts (like us) can make sure your tools are running correctly every day. Every single day our backups are verified to ensure your system can be recovered no matter the disaster situation.

We put extra safeguards in place such as continuous data protection (CDP). CDP continuously saves changes to your files, allowing you to go back in time and restore your data as it was just before an attack or loss.
You may think because your files are saved in Microsoft, Google, DropBox or any number of other cloud services your files are safe, and Microsoft is taking care of the backups. This is not the case, and you still need a separate encrypted and secure backup. Whether your files are all in the cloud, on-premises or a combination of the two, backup is critical.
This is something we do for businesses like yours every day. Reach out if you are concerned about your existing backup solution or if you have any questions. Contact us at (319) 535-5350 or [email protected] to setup an appointment.
Picture this: You’re having a busy day at work when the phone rings. On the other end of the line is someone claiming to be from Microsoft Teams support. They sound professional, helpful even. But before you follow their instructions, ask yourself: could this be a scam?
The latest trend in cybercrime involves scammers posing as “help desk” staff to trick employees into granting access to their devices. It’s part of a larger ransomware strategy designed to lock businesses out of their own data until they cough up a hefty ransom. These attacks are devastating and growing in sophistication.

Recently, a notorious cybercrime group took this scam to a whole new level. Here’s how their operation works:
But it doesn’t stop there. These scammers are also leveraging Microsoft Teams to gain trust. They’ll create fake Teams accounts with usernames like “Help Desk” and domains such as “securityadminhelper.onmicrosoft.com.” Then, they send one-on-one messages to employees, claiming they need access to their devices to resolve an issue.
Ransomware attacks are more than just an inconvenience; they’re a direct threat to your operations, reputation, and bottom line. Here’s what’s at stake:
Education and vigilance are your first lines of defense. Share this information with your team and encourage a healthy skepticism toward unsolicited calls or messages. Here are a few specific steps to safeguard your business:
Ransomware is serious business, but it doesn’t have to become your business’s problem. By staying informed and proactive, you can protect your operations, your customers, and your reputation. If you’re unsure whether your systems are as secure as they could be, we’re here to help. Get in touch today to discuss your cybersecurity strategy and ensure your business is prepared for whatever comes next.
Ever feel overwhelmed by the maze of chats, channels, and notifications in Microsoft Teams? Well, here’s the good news: Microsoft’s rolling out an update to help streamline things.

The update will create a simpler workspace that’s easier to navigate – grouping everything in one location under the Chat menu. Think of it as a central hub where all your key conversations and notifications live.
The update also includes a new “@mentions” view that gathers all your direct messages and important mentions in one place. This will make it easier to catch up on messages you’re tagged in, helping you to make sure important notifications don’t slip through the cracks.
Teams will also be getting improved filters and controls. This will let you do things like filter out less urgent notifications, as well as create custom sections to keep your chats, channels, and meetings organized by project or topic.
Another great feature being introduced is a new “favorites” section, allowing you to pin your top chats and channels for quick access.
Also, threaded conversations are expected to arrive some time in mid-2025. This will mean that replies get grouped together in the same thread, making it easier to follow discussions without losing track of previous messages.
All these improvements are coming to desktop, Android, and iOS – so your team will be able to stay on top of things no matter where they are.
If you’re not already using Teams to keep communication flowing in your business, now’s a great time to start. We can help with that, get in touch.
AI chatbots have taken the world by storm in recent months. We’ve been having fun asking ChatGPT questions, trying to find out how much of our jobs it can do, and even getting it to tell us jokes.
But while lots of people have been having fun, cyber criminals have been powering ahead and finding ways to use AI for more sinister purposes.
They’ve worked out that AI can make their phishing scams harder to detect – and that makes them more successful.

ChatGPT Bad Jokes
Our advice has always been to be cautious with emails. Read them carefully. Look out for spelling mistakes and grammatical errors. Make sure it’s the real deal before clicking any links.
And that’s still excellent advice.
But ironically, the phishing emails generated by a chatbot feel more human than ever before – which puts you and your people at greater risk of falling for a scam. So, we all need to be even more careful.
Crooks are using AI to generate unique variations of the same phishing lure. They’re using it to eradicate spelling and grammar mistakes, and even to create entire email threads to make the scam more plausible.
Security tools to detect messages written by AI are in development, but they’re still a way off.
When someone leaves your business, you might be so wrapped up in the rush of everyday tasks, you forget to delete their login details, which can affect your security login processes.

It’s easy to overlook. You’ll get around to it later, right?
But unused login details could be a ticking time bomb for security breaches, leaving the doors wide open to cyber criminals. It can also be an unnecessary drain on your budget if you’re paying for old subscriptions you no longer need.
A recent report found that almost half of businesses had accounts that were no longer actively managed, which can undermine your security login protocols.
If you’ve forgotten about an account, you’re not monitoring it. And this leaves your business vulnerable to attacks.
These risks aren’t just hypothetical, either. Many cloud security breaches happen because unused login details and accounts have been compromised.
So, what do you need to do?
Take the time to audit all accounts and login details used by your business. Make sure you no longer have accounts open for ex-employees (and check that their access has been fully revoked, not just left inactive) to avoid security login issues.
The same goes for any software or service that you’ve stopped using in your business. You might not realize you’re still paying for a service you haven’t touched in months – or even years.
Going forward, make sure you have a clear process for when people leave, and regularly review the applications and services your business uses.
If you’re not sure where to start, let us help you perform a security review and make sure you’re not leaving your business exposed to unnecessary threats. Contact us at (319) 535-5350 or [email protected] to setup an appointment.
On August 6th, 2024, most, if not all, of the US population’s personal information was leaked by hackers that stole the information from National Public Data back in April. According to NPD’s website, they provide criminal records, background checks and more; the more may now include helping hackers take over your identity.
What does this mean for the average American? Not a lot really. So many breaches have happened over the past several years that almost all our data is and was already for sale on the Dark Web. The only difference here is that the hacking group responsible, USDoD, published the complete list and made it available for free.
This will certainly lead to even more scammers and hackers using this data for nefarious purposes. The data leaked included name, mailing address, Social Security Numbers, and date of birth. This data can easily be combined with other hacked data sources to connect email addresses, passwords, and other sensitive information to create what hackers call a FULLZ, slang for “full information” on you.
Should you do anything to better protect yourself from these hackers and scammers? 100% YES. The top three things you should do, in priority, are as follows.
You should freeze your credit today. It keeps a scammer from being able to take out credit in your name, which is the most damaging aspect of identity theft. There is no reason not to do it. The three primary credit reporting bureaus are Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. They all do this for free and it is easy to unfreeze and refreeze when you want to buy a new car, open a credit card, or refinance your house.
If you don’t want to spend any money, there are free ones available in Google Chrome or Apple Keychain. Better yet, spend a few bucks and buy 1Password, Bitwarden or Keeper. Wired has a great article on the best options for free and paid along with reasons to use a paid version.
This sounds counter intuitive, but for every financial service you have, banking, brokerage, 401K, 529, etc., you need to sign up for the online service. It is much easier for a hacker to sign up for these online services than it is to crack, steal or otherwise connive you out of an existing username and password. Especially if you use a password manager and every password for every login is different and 24 random characters. You only need to remember one password.
Bottom line you need to take personal responsibility for securing your identity regardless of what the next big breach is, and there will be another. It is not a question of if, but when.
Image: This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the role of the system administrator within small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) has undergone a massive transformation. A decade ago, the one “tech guy" sitting alone in the server room could manage almost all aspects of an organization’s IT infrastructure. Today, the complexity and scale of IT systems demand a more specialized approach. This shift has not only reshaped the role of the system administrator but also the strategies SMBs must adopt to manage their technological needs effectively.
The "Jack of All Trades" Era
Traditionally, system administrators in SMBs were generalists, often single-handedly managing a wide array of IT responsibilities—from setting up and maintaining network operations, managing server environments, to overseeing security protocols and software deployments. They were the go-to problem solvers, adept at patching together solutions and making the most out of limited resources. The scope of their role required broad, but not necessarily deep, knowledge across various IT domains.
My First Sys Admin Role
The first Systems Administrator role for me was within a financial services company of forty employees. This was before compliance and cybersecurity concerns. Their Internet connection was delivered via a bank of dial up modems. Email was new and hackers couldn’t use Bitcoin to ransom the entire system. This was over 25 years ago.
Bitcoin Changed Everything
Once Bitcoin became mainstream, at least within the hacker community, the security and IT landscape was changed forever. Bitcoin was initially released on January 3, 2009, but wasn’t widely used until around 2012. With Bitcoin, hackers could start getting paid anonymously anywhere in the world. This led to the explosion of cybercrime and exponentially increased the need for specialized talents within technology.
Transition to Specialization
Over the past decade, several key factors have driven the need for more specialized IT roles within SMBs:
1. Technological Complexity
The IT landscape has grown exponentially in complexity with advancements in cloud computing, big data, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. Technologies that were once optional or considered "luxuries" for SMBs have become necessities in maintaining competitive advantage and operational efficiency.
2. Security Concerns
With the increase in cyber threats, security has become a top priority for businesses of all sizes. The growing sophistication of cyber-attacks requires expertise not just in preventive measures but also in rapid response and recovery strategies. This has led to the need for roles specifically focused on cybersecurity within SMBs.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Changes in regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS have significant implications for how data is managed and protected. Compliance requires specialized knowledge to navigate the legal and technical requirements, pushing the system administrator role toward specialization.
4. Cloud and Hybrid Environments
The shift towards cloud-based services and hybrid environments demands a deep understanding of cloud service models, integration, and management. System administrators must now possess specific skills in managing these environments, which often include multiple service providers and platforms.
New Skills and Roles
As a result of these changes, the system administrator’s role is branching into more specialized domains:
Implications for SMBs
For SMBs, this transition means rethinking how they staff and manage their IT departments. While larger organizations might afford the luxury of several specialized roles, SMBs often need to find a balance. This may involve:
The era of the "one tech guy" who could do it all is becoming a relic of the past for SMBs. As technology continues to advance at a breakneck pace, the role of IT professionals within these organizations is becoming more specialized. SMBs must adapt to this reality by either developing their own expertise or strategically outsourcing, ensuring that their businesses can not only survive but thrive in the digital age. The future of SMB IT management is specialized, nuanced, and undeniably complex, but with the right strategy, also tremendously rewarding.